What role does the servo controller play in a servo system
The servo controller ensures not only that the servo motor moves to the desired position at the right speed, but also takes on an increasingly important role in the servo system. In this article, we briefly touch upon the development of the servo controller, discuss its individual components, and explore how to choose the right servo controller for your application.
What is a servo controller

The servo controller is an electronic device that ensures the correct current and voltage are supplied to the servo motor based on a reference signal, allowing it to move at the desired speed and to the desired position. Servo controllers are available in various configurations, voltage and current values, and can perform position, speed, and torque control.
A wide range of servo motor types can be controlled using servo controllers, including AC, DC, brushed, brushless, rotary, or linear servo motors. Additionally, the servo controller includes a system to protect against overload of both the servo motor and the controller itself. A servo controller is an integral part of an electromechanical servo system.
Development of the servo controller
The electric motor has been used since the late 19th century, but it wasn’t until the 1970s that the digital servo controller as we know it today came into existence. The ability to amplify signals in voltage and current and to control position, speed, and current has led to various technical solutions throughout history due to practical challenges. Initially, signal amplification was done using an amplidyne, and after the development of solid-state electronics, transistors, MOS-FETs, and IGBTs were used. Initially, servo controllers were analog in nature, and after the development of digital electronics, programmable ICs were employed. With the increasing processing power available today, the functionality, reliability, and accuracy of the servo controller continue to improve.
Components of the servo controller
The servo controller generally consists of the following components:
1. Power stage or power circuit.
2. Control circuit.
3. Current, speed, and position controllers.
4. Interface with the control system.
5. Feedback circuit.
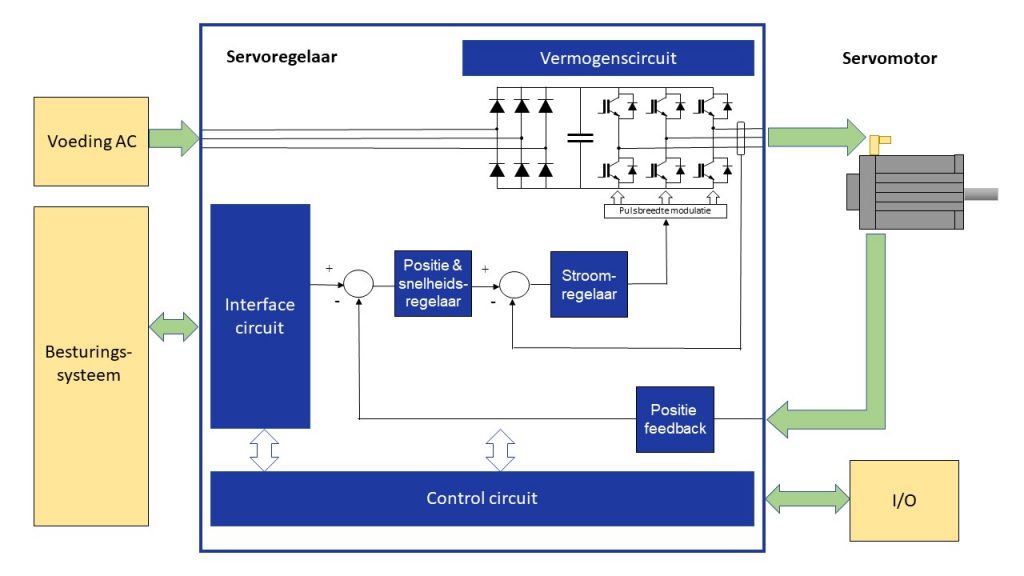
An important function of the servo controller is to provide the correct current and voltage to the servo motor. For this purpose, the servo controller contains a power stage or power circuit. This component ensures that the connected mains voltage to the servo controller is rectified and filtered. Through the inverter, the appropriate amount of current and voltage is then delivered to the windings of the servo motor using pulse-width modulation.
Because the torque or force produced by the servo motor is proportional to the current through the motor windings, the servo controller includes a current regulator. The current regulator receives its reference signal from the position and speed controllers.
The position and speed controllers, in turn, receive their reference signal from a profile generator. This profile generator is located within the servo controller or the control system.
The various controllers and control loops within the servo controller are crucial for the performance of the servo system. These controllers ensure that the system’s output closely follows the input, that the system is stable, and that it is robust against external disturbances. To achieve the desired dynamic behavior, in addition to the different controllers, there are often feedforward loops, low-pass filters, notch filters, and/or B-quad filters available. Tuning or adjusting the servo controllers is a specialization that often involves a form of “autotuning” within modern systems.
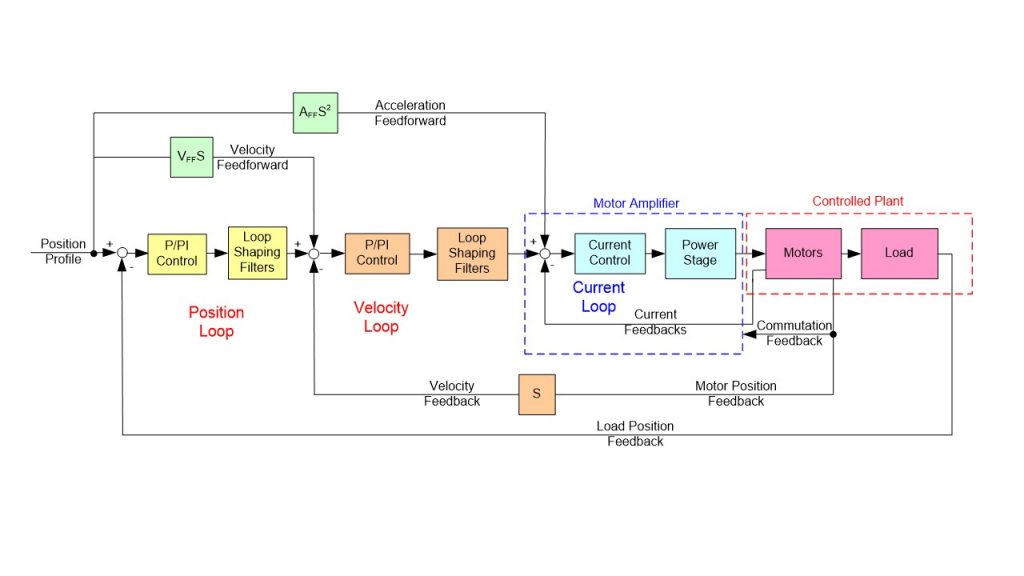
The control system communicates with the servo controller through an industrial bus system. The bus systems used within servo control include EtherCAT, ProfiNet, CanOpen, PowerLink, and DeviceNet. The communication protocol can be based on “IO” control or Softmotion control.
The feedback circuit measures the actual position of the servo motor and/or the tool using a position sensor. This position measurement system consists of an encoder or a resolver. A resolver is a rotary sensor placed in a servo motor that provides an absolute position over one revolution. An encoder comes in incremental and absolute variants. Nowadays, an encoder with a digital interface like Hyperface DSL or EnDat is commonly used. Besides reading the actual position, it’s also possible to store specific motor data in the encoder for the servo controller to read. This information is used to automatically implement the settings for that motor in the controller.
The control circuit handles all potential I/O interactions such as limit switches and home switches. Additionally, the control circuit monitors the necessary parameters for the safety of the servo controller and the servo motor.
Expansion of servo controller functionality
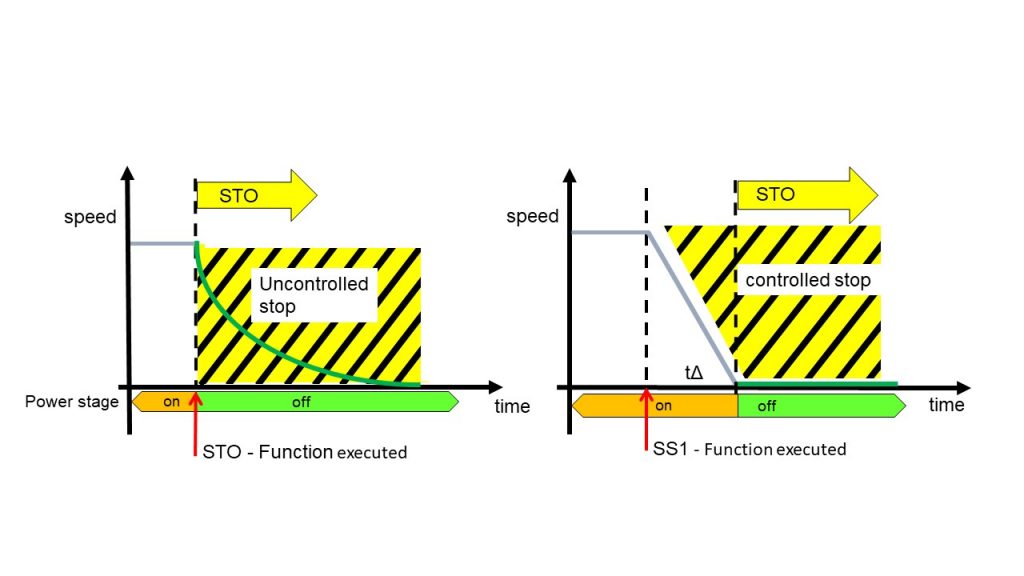
Beyond the described functionality of controlling and regulating position, speed, and torque, additional functionality can be added to a servo controller. This might include safety features such as Safe Torque Off (STO) and Safe Stop (SS1). These functions ensure that when a sensor, for instance, is activated, the servo system transitions to a defined safe state.
Other functionality that can be added to the servo controller includes creating registration positioning movements. In this scenario, the servo system, already in motion, will move to a defined position upon initiation by a hardware input. Activating and executing this movement is done from the servo controller because registering the position of the servo system is most accurately achieved from the servo controller.
Calculating Servo Motor and Servo Controller
Calculating and selecting a servo motor and servo controller is the specialization of VARIODRIVE. The application specifications, environmental conditions, and any other requirements determine the configuration of the servo system and thus the type of servo controller. Tuning or adjusting a servo controller requires a good understanding of control engineering and mechatronics, which is an area in which the application engineers at VARIODRIVE are highly skilled.
We are happy to discuss your application and share more about how we would approach the motion control challenge. Our experience with a wide variety of applications and our knowledge of various components enable us to add value even in initial, non-obligatory conversations. Contact us at sales@variodrive.nl or call +31 186636280 to schedule an appointment.
